vet-toon: Rabbit’s body language
Understanding rabbit behaviour
Your
rabbit’s body language can help you to understand how they are feeling.
Rabbits
have great hearing and can rotate their ear independently. Their ears are also
a quick guide to how they feel.
- Forward: curious
- Upright: alert
- Backwards 45 degrees: relaxed
- Laid back further: nervous or aggressive
A
rabbit posture, the way they sit or stand, is a big clue to what they are
thinking – particularly for lops who don’t move their ears much.
- Rabbits lean forwards to investigate
- Rabbit lean away from scary things.
Pay
attention to changes in normal hopping motion.
- They go faster when excited or running away
- They go lower when being cautious. Cautious or scared rabbits also keep their body closer to the ground when moving.
A
happy rabbit.
These rabbits are
relaxed and happy
- Rabbits show ears close together, facing slightly backwards and pointing outwards. Eyes may be partially closed.
- Rabbit is lying down, with a relaxed body posture and legs tucked under body.
- Rabbit is lying down, with the front paws pointing forward and rear legs stuck out sideways. Body is relaxed and extended.
- Rabbit is lying down with the fully extended, relaxed body. Back legs are stretched out behind the body and the front paws are pointing forward.
- Rabbit jumps into the air with all four paws off the ground and twists in mid-air before landing.
- A relaxed rabbit will rest their ears back about 45 degrees, sit or lay comfortably and move with a steady hop. When napping, the more difficult the position is to get up from, the more relaxed they are.
Sleepy
When
rabbits are napping, and not paying any attention to their surroundings, they
lay down, stop twitching their nose and rest their ears back on their body.
Curious
Curious
rabbits cup their ears towards what they are exploring, twitch their nose
rapidly and lean or stretch forwards to get a better look. They move slowly,
creeping on tiptoes, instead of hopping.
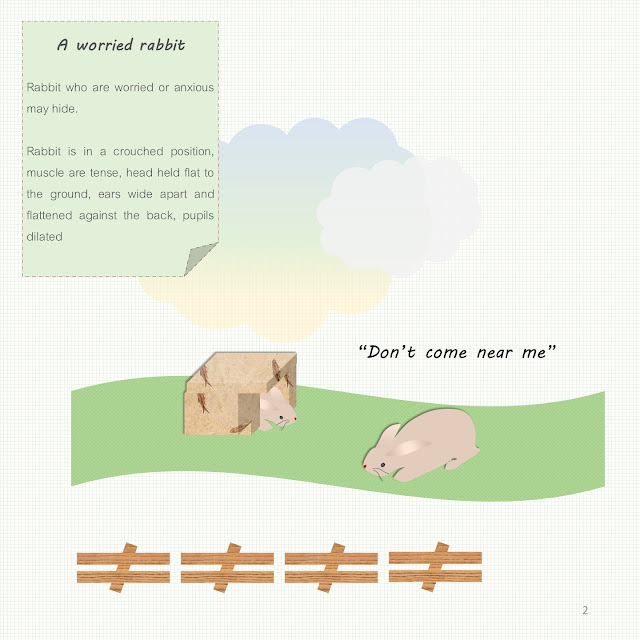
A
worried rabbit
These
rabbit are telling you that they are uncomfortable and don’t want you near
them.
Rabbit
is in a crouched position, muscles are tense, head held flat to the ground,
ears wide apart and flattened against the back, pupils dilated.
Rabbits
who are worried or anxious may hide.
Alert
An
upright posture and ears pointed straight up mean your rabbit is alert and
paying attention to something. Alert rabbits freeze in position, but may swivel
their ears and twitch their nose rapidly. They are ready to flee (or head for
the treat jar) as soon as they work out what is going on.
Nervous
A
nervous rabbit will lean or turn away from the threat, crouch down to make
themselves harder to spot, but still be ready to run. Their ears are folded and
pointed back, they may freeze, bolt for cover or turn aggressive if cornered.
Aggressive
A
rabbit ready to attack will try to make themselves appear bigger by rising
their body, chin and tail. Their ears are folded and pointed back over their
shoulders. They move forward in quick dashes, often growling.
An
angry or very unhappy rabbit
These
rabbits are not happy and want you to stay away or go away.
- Rabbit turns and moves away flicking the back feet. Ears may be held against the back.
- Rabbit is sitting up on back legs with the front paws raised displaying boxing behaviour. Ears pointed upwards and facing outwards. Rabbit may be growling.
- Rabbit is standing tense, with back legs thumping on the ground. Tail raised, ears pointing upwards and slightly turned outwards, facial muscles are tense and pupils dilated.
- Rabbit is standing tense with body down and weight towards the back, head tilted upwards, mouth open and teeth visible. Ear held back and lowered, tail raised, pupils dilated.
Reference:
Royal
Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals. www.rspca.org.uk
Stone,
T. Behaviour: What your rabbit is feeling. www.theRabbitHouse.com



















Komentar
Posting Komentar